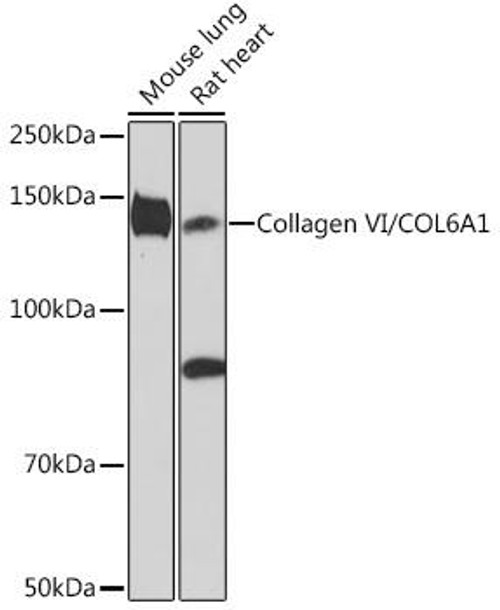
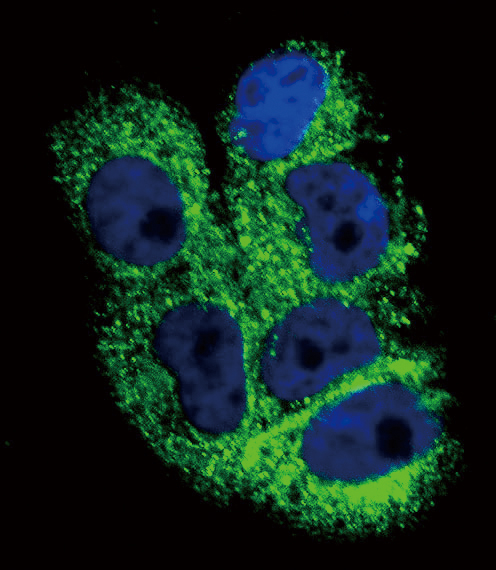
TTD/XP-D confluent fibroblasts show a reduced amount of COL6A1. ( A and... | Download Scientific Diagram
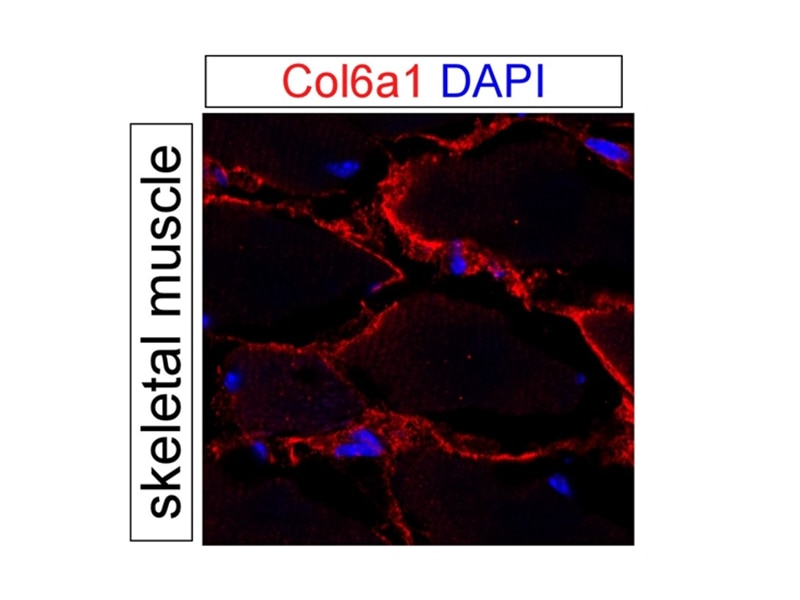
Col6a1 Null Mice as a Model to Study Skin Phenotypes in Patients with Collagen VI Related Myopathies: Expression of Classical and Novel Collagen VI Variants during Wound Healing | PLOS ONE
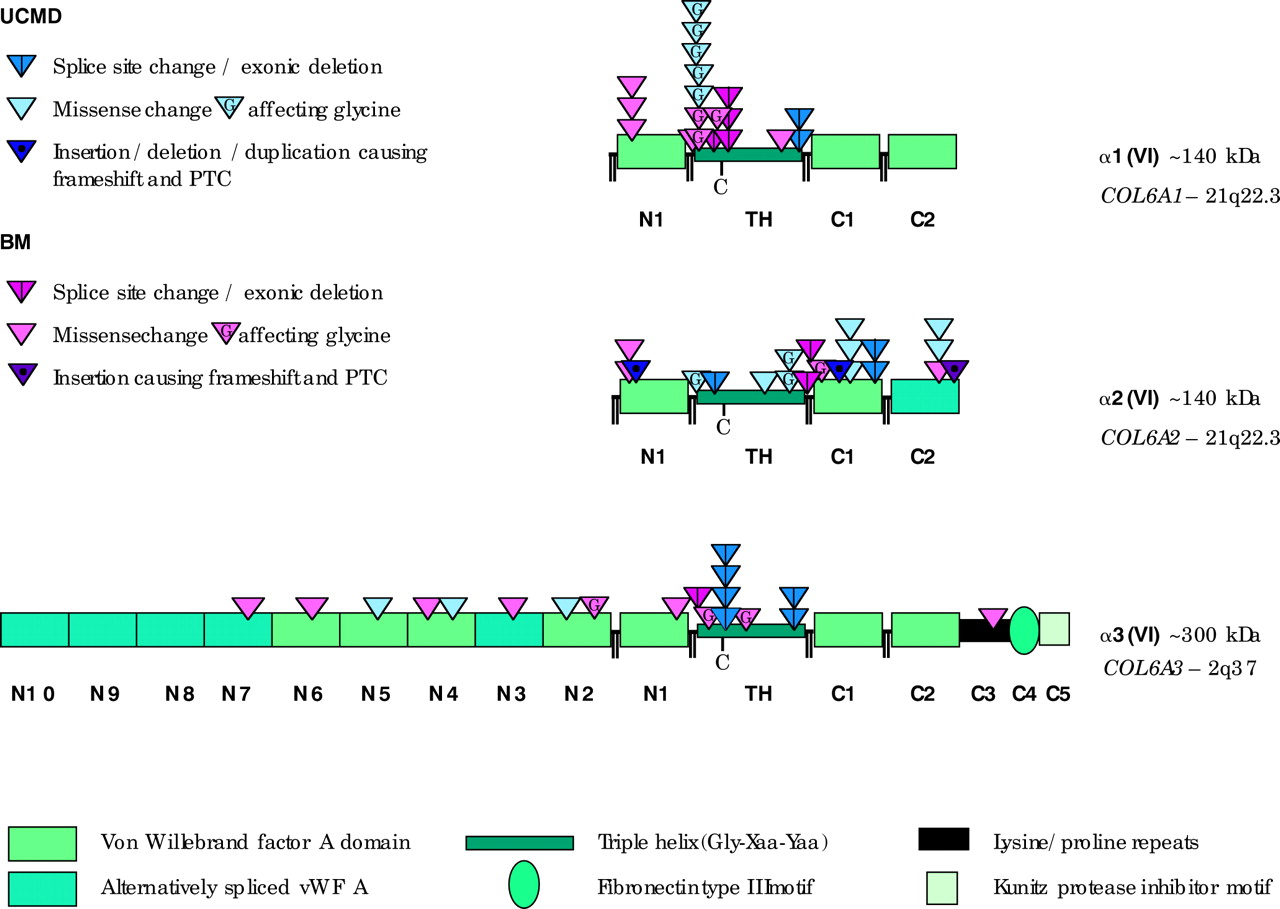
Automated genomic sequence analysis of the three collagen VI genes: applications to Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy and Bethlem myopathy | Journal of Medical Genetics

Repartition of the various types of mutations identified in the COL6A1,... | Download Scientific Diagram
COL6A1 expression affects the prognosis of patients with pancreatic... | Download Scientific Diagram
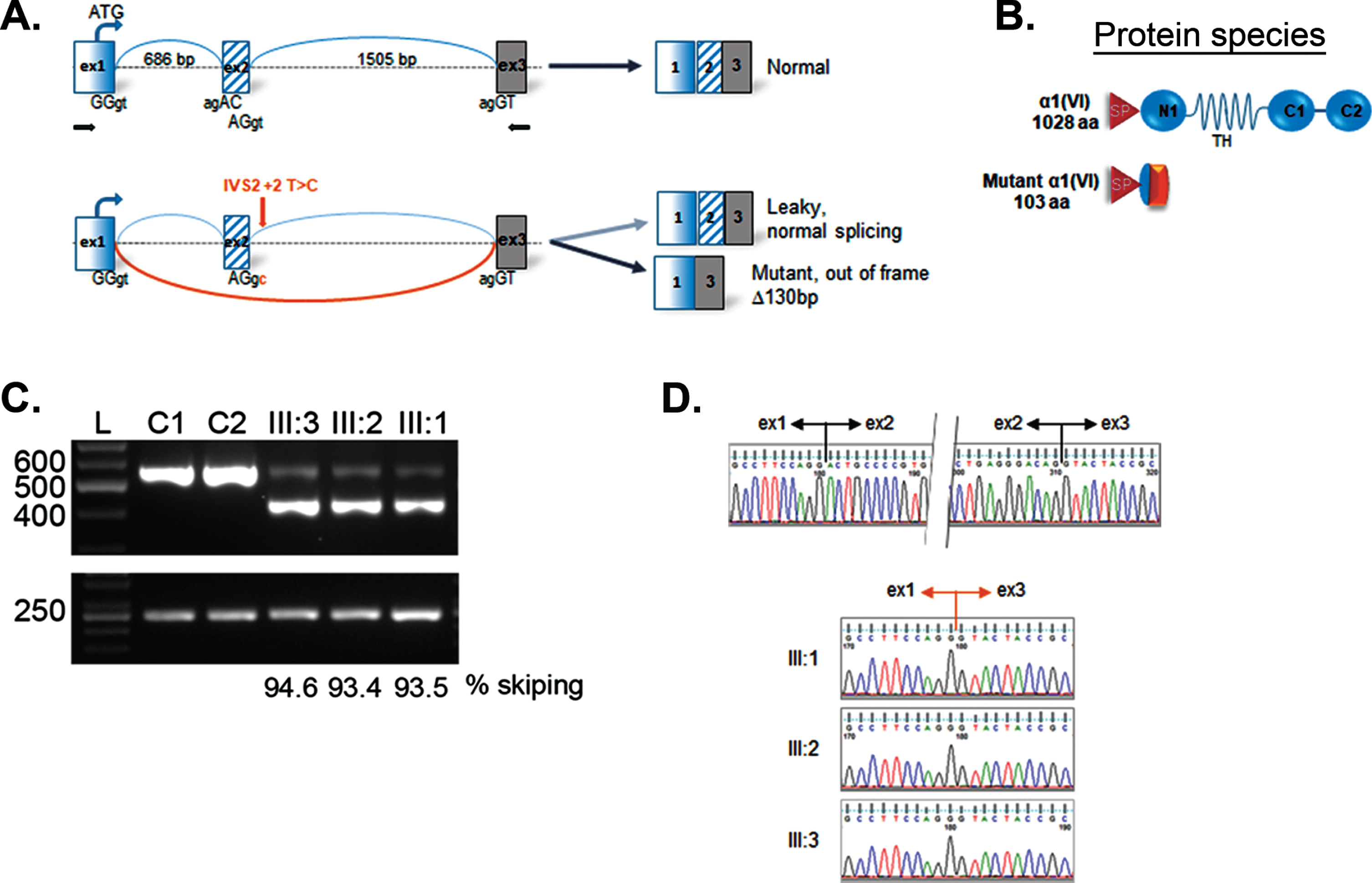
Intrafamilial Phenotypic Variability of Collagen VI-Related Myopathy Due to a New Mutation in the COL6A1 Gene - IOS Press
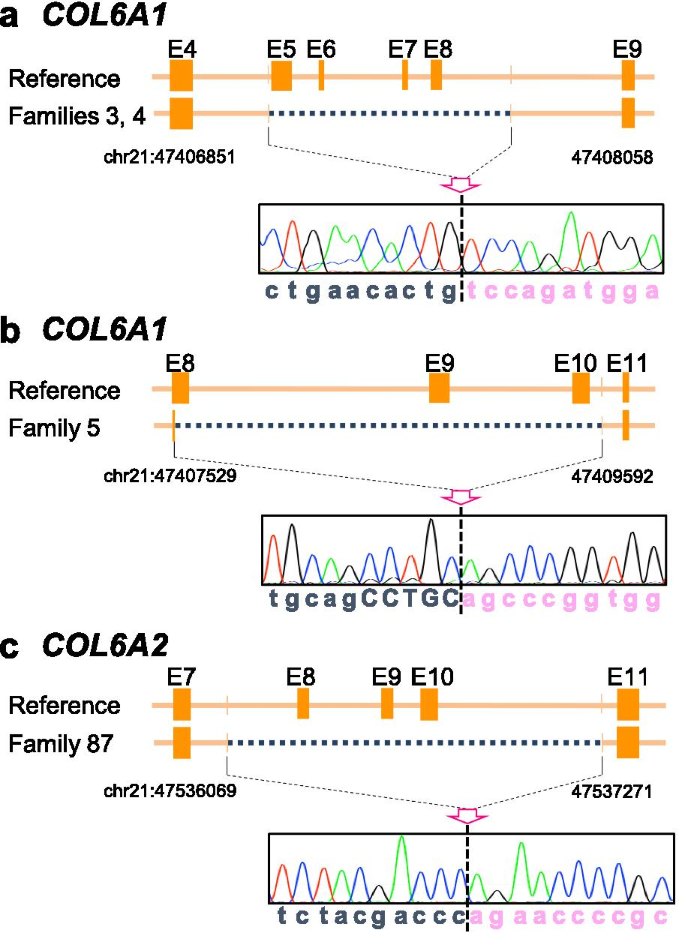
Causative variant profile of collagen VI-related dystrophy in Japan | Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases | Full Text
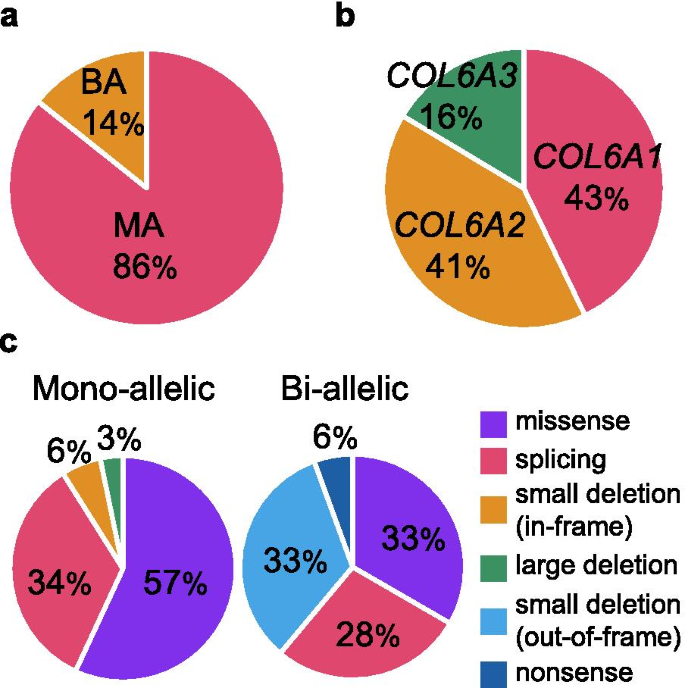
Causative variant profile of collagen VI-related dystrophy in Japan | Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases | Full Text

Exon-Skipping Oligonucleotides Restore Functional Collagen VI by Correcting a Common COL6A1 Mutation in Ullrich CMD - ScienceDirect